In the world of networking, computers don’t go by names like us, they go by numbers because that’s how devices talk and identify each other such as IP addresses. DNS (Domain Name System) helps resolve names to numbers to be more specific, it resolves domain names to IP addresses. So, if you type a web address in a browser the DNS will resolve that name to a number because the only thing computers understand is numbers.
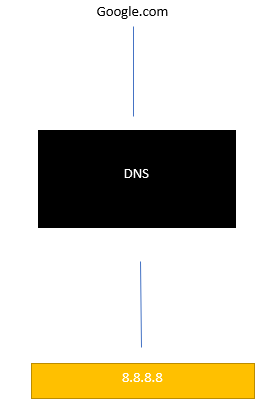
If you type in google.com in your browser, the DNS server will search through its database to find a matching IP address for that domain name, when it finds it, DNS will resolve it to the matching IP address, once it is completed then your computer will be able to communicate with Google’s webserver to retrieve its webpage. It works like a phone book, when you want to find a number, you don’t look up for number first, you look for the name, and then you will find the number associated with the name.
So, let’s dive in and see what happens backstage when you type in the web address on the computer.

Once the web page is loaded on your computer it will be stored in its cache memory in case it receives another query for google.com, which means it won’t go on a quest for google.com again.